Ping:
- The command ping send an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity.
Tree:
- The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path.
FTP:
- ftp command is used to transfer file to and from another computer.
- The remote computer must be operating an FTP server.
- You can open list of all the drivers installed on your PC with just a single command.
- Just type “driverquery” in the Command Prompt and press Enter. After a short delay, you will see all the drivers installed in your PC along with, Name, Type and Link date.
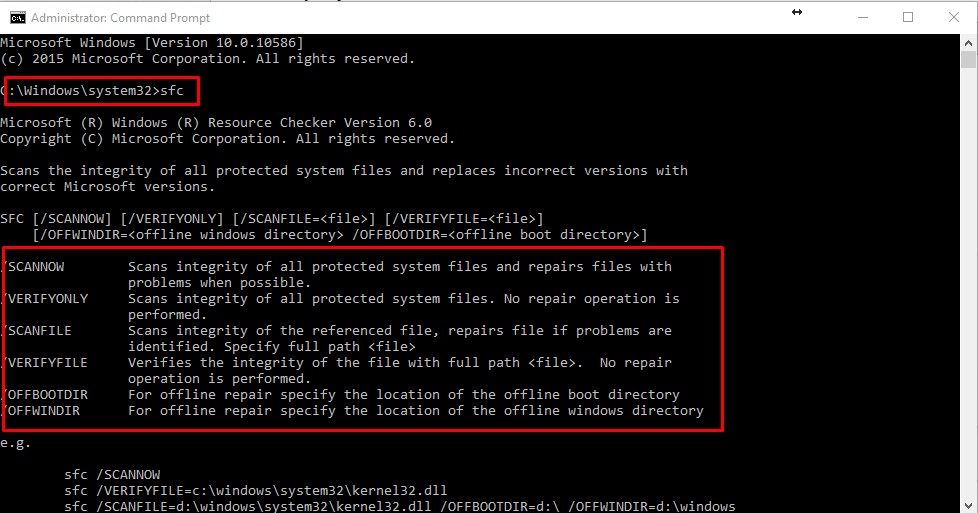
sfc/scannow:
- The system files can also be scanned and repaired from the Command Prompt. Type “sfc/scannow” and press enter, the scan will start and may take quite some time depending on your PC speed (up to an hour may be).
- It will either automatically repair the files or let you know if there is a problem and provide its details.
- You can create un deletable folders using specific set of keywords. In the Command Prompt, type the name of the drive where you want to create the folder (it must not have Windows installed in it). After that, type any of these keywords “md con\” or “md lpt1\” and press Enter. So it should look something like this “D: md con\”.
- This will create a folder with the same name that could not be deleted or renamed. To delete the folder replace “md con\” with “rd con\” or “md lpt1\” with “rd lpt1\”.
attrib:
- You can hide folder with the help of Command Prompt that cannot be accessed using the traditional hide feature of Windows. To do this, type the drive name where the folder is located and then enter this command “Attrib +h +s +r” and afterwards, enter the name of the file/folder you want to hide. So it should look something like this “D: Attrib +h +s +r haider”.
- If the folder is inside another folder, then the command must come before the folder/file you want to hide not just after the Drive name. To again see the folder, use the same process above but change the command to “Attrib -h -s -r” from “Attrib +h +s +r”.
- Windows 8.1 removes the Windows 7 backup interface, which allowed you to create system backup images.
- These system images contain a complete snapshot of every single file on the system, so they’re different from Windows 8’s recovery images.
telnet – Connect to Telnet Servers:
- The telnet client isn’t installed by default. You’ll have to install it from the Control Panel. Once installed, you can use the telnet command to connect to telnet servers without installing any third-party software.
- You should avoid using telnet if you can help it, but if you’re connected directly to a device and it requires that you use telnet to set something up — well, that’s what you have to do.
cipher – Permanently Delete and Overwrite a Directory:
- The cipher command is mostly used for managing encryption, but it also has an option that will write garbage data to a drive, clearing its free space and ensuring no deleted file can be recovered.
- Deleted files normally stick around on disk unless you’re using a solid state drive. The cipher command effectively allows you to “wipe” a drive without installing any third-party tools.
- The netstat command is particularly useful, displaying all sorts of network statistics when used with its various options.
- One of the most interesting variants of netstat is netstat -an, which will display a list of all open network connections on their computer, along with the port they’re using and the foreign IP address they’re connected to.